
The few exceptions to this guideline are very light ions derived from elements with precisely known atomic masses. Even when calculating the mass of an isolated ion, the missing or additional electrons can generally be ignored, since their contribution to the overall mass is negligible, reflected only in the nonsignificant digits that will be lost when the computed mass is properly rounded. Moreover, the mass of an electron is negligibly small with respect to the mass of a typical atom. Even though a sodium cation has a slightly smaller mass than a sodium atom (since it is missing an electron), this difference will be offset by the fact that a chloride anion is slightly more massive than a chloride atom (due to the extra electron). This approach is perfectly acceptable when computing the formula mass of an ionic compound. Note that the average masses of neutral sodium and chlorine atoms were used in this computation, rather than the masses for sodium cations and chlorine anions. Table salt, NaCl, contains an array of sodium and chloride ions combined in a 1:1 ratio. Spectroscopic and Magnetic Properties of Coordination CompoundsĪldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters

Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Transition Metals and Their CompoundsĬoordination Chemistry of Transition Metals Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of the Noble Gases Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Halogens Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Sulfur Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Oxygen Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Phosphorus Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Nitrogen Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Carbonates Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Hydrogen Structure and General Properties of the Nonmetals Structure and General Properties of the Metalloids Occurrence and Preparation of the Representative Metals Representative Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals The Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics Shifting Equilibria: Le Châtelier’s Principle Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature: The Ideal Gas Law Periodic Variations in Element Properties Mathematical Treatment of Measurement Resultsĭetermining Empirical and Molecular FormulasĮlectronic Structure and Periodic Properties of ElementsĮlectronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations) But the most convenient way is to write the chemical formula and then evaluate.Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision Molar can be obtained using various practical lab experimentations as well. Magnesium phosphate exists in three forms, but the mostly stable and organically found form is Magnesium triphosphate. For many it is exactly double to the number of electrons present in that particular atom.
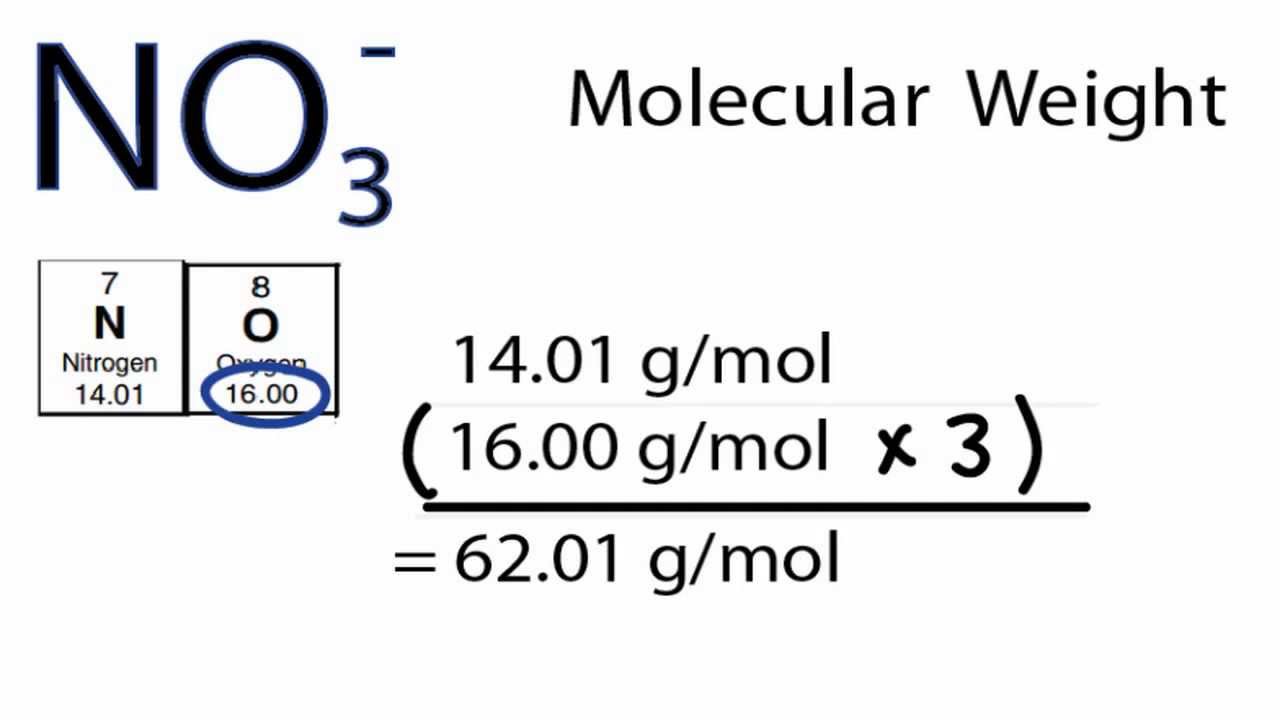
The mole of every substance is different. It is the measure of an amount of substance in its one unit which represents all the properties of that element. Note: We have to remember that the mole is the smallest unit of an element. Magnesium phosphate are found in general, in three forms, namely as, Hint: We have to remember that the magnesium phosphates are chemical compounds referred to as sails of magnesium and phosphate which exist in different forms and hydrates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
